More than just a gluten-free diet, coeliac disease is a serious and life-long autoimmune condition that, if not properly managed, can have devastating effects on a person's physical and mental health, and lead to other life-threatening complications.
What is Coeliac Disease?
Coeliac disease is a chronic autoimmune condition affecting about 1 in 70 Australians. It is characterised by an abnormal immune response to gluten, a protein that is found in wheat, rye, oats, triticale and barley (Better Health Channel 2021).
Gluten contains a component known as a prolamin fraction, which is responsible for triggering the abnormal immune response. Different grains each have a different prolamin fraction:
- Gliadin (wheat)
- Secalin (rye)
- Hordein (barley)
- Avenin (oats).
(Better Health Channel 2021)
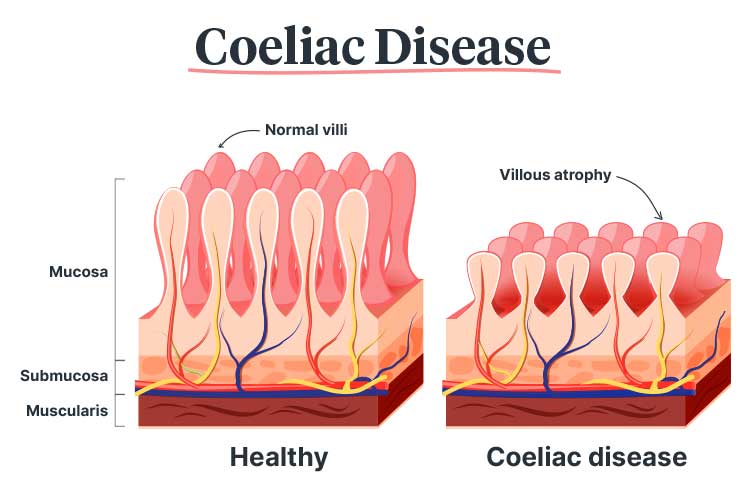
When a person living with coeliac disease eats even a tiny amount of gluten, it triggers an immune response that damages the villi - tiny, finger-like projections that increase the surface area of the small intestine (Better Health Channel 2021).
The villi are responsible for breaking down and absorbing nutrients, vitamins, minerals, fluids, and electrolytes from food. However, in someone with coeliac disease, exposure to gluten triggers the production of autoantibodies that target the villi. This causes the villi to become inflamed and flattened in a process known as villous atrophy, greatly reducing the surface area of the small intestine that is able to absorb nutrients (Better Health Channel 2021; Daley & Haseeb 2025).
Damage from this immune response may result in various symptoms that impair health and quality of life (Healthy WA 2018).
What Causes Coeliac Disease?
Almost every person who develops coeliac disease has one or both of two particular genes: HLA-DQ2 and HLA-DQ8 (Daley & Haseeb 2025).
This genetic predisposition is common, with about 50% of Australians being born with HLA-DQ2 and/or HLA-DQ8. Despite this, only about 1 in 40 people will actually develop coeliac disease (Better Health Channel 2021).
In order for coeliac disease to develop, it appears that HLA DQ2 and/or HLA DQ8 must be triggered by an environmental factor such as diet or a previous gastrointestinal infection. Coeliac disease can develop at any age (Better Health Channel 2021; Healthdirect 2024).
Coeliac disease is a hereditary disease. While the inheritance pattern is unknown, first-degree relatives (parents, children and siblings) of someone with coeliac disease have a 10% chance of developing the condition themselves (MedlinePlus 2019; Better Health Channel 2021).
Comorbidities that appear to increase the risk of developing coeliac disease include:
- Type 1 diabetes
- Ulcerative colitis
- Certain neurological disorders (e.g. epilepsy)
- Thyroid disease
- Down syndrome.
(Healthdirect 2024)
Interestingly, coeliac disease appears to be more common in people of European descent (Daley & Haseeb 2025).
Symptoms of Coeliac Disease
The symptoms of coeliac disease can range from minor, to severe, to unnoticeable in some cases. Coeliac disease is often underdiagnosed and symptoms may be misinterpreted as irritable bowel syndrome, food sensitivity, stress or age (Better Health Channel 2021; Healthdirect 2024).
Potential symptoms include:
- Diarrhoea or constipation
- Fatty stools
- Nausea and vomiting
- Flatulence
- Bloating
- Abdominal pain and discomfort
- Nutritional deficiencies
- Weight loss
- Persistent fatigue
- Irritability
- Failure to thrive, developmental delay or delayed puberty (in children)
- Pain and stiffness in bones or joints
- Dental problems, including recurring mouth ulcers.
(Healthdirect 2024; Daley & Haseeb 2025)

How is Coeliac Disease Diagnosed?
Indications for coeliac disease testing include:
- Gastrointestinal symptoms
- Malabsorption of nutrients as indicated by a blood test
- Early osteoporosis
- Infertility with no known explanation
- Family history of coeliac disease
- Liver disease
- Down syndrome or Turner syndrome
- Dermatitis herpetiformis
- Neurological symptoms of unknown origin
- Autoimmune disease (e.g. type 1 diabetes, autoimmune thyroid condition).
(Pathology Tests Explained 2024; Healthdirect 2024)
The diagnosis of coeliac disease involves autoantibody testing. The tests typically used are:
- Transglutaminase IgA antibody (iTG-IgA)
- Anti-gliadin antibodies.
(Pathology Tests Explained 2024)
Diagnosis should be confirmed via a biopsy of the small intestine in order to determine whether there is any damage to the villi. This is performed using gastroscopy (Healthdirect 2024).
Genetic tests to detect a genetic predisposition for coeliac disease may be performed if there is uncertainty about the patient’s diagnosis. However, these tests alone cannot diagnose coeliac disease as HLA-DQ2 and/or HLA-DQ8 are found in half of the population. Despite this, they may be useful in ruling out coeliac disease as a potential diagnosis (Pathology Tests Explained 2024; Healthdirect 2024).
Once coeliac disease has been diagnosed, some patients may undergo additional testing in order to determine the severity and extent of the condition, such as:
- Full blood count to detect anaemia
- CRP (C-reactive protein) to identify inflammation
- ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) to identify inflammation
- Electrolytes and LFTs (liver function tests) to evaluate electrolyte, protein and calcium levels, along with kidney and liver status
- Vitamin D, E and B12 and folate testing to identify any vitamin deficiencies
- Iron studies
- Allergy testing.
(Pathology Tests Explained 2024)
Complications of Coeliac Disease
Coeliac disease can have serious complications if not managed properly. These may include:
- Osteoporosis
- Infertility and miscarriage
- Malnutrition
- Depression and anxiety
- Dental issues
- Lactose intolerance
- Liver disease
- Nervous system problems (e.g. seizures, peripheral neuropathy)
- Increased risk of certain cancers (rarely), for example, lymphoma of the small intestine.
(Daley & Haseeb 2025; Mayo Clinic 2023)
These complications can generally be avoided if coeliac disease is diagnosed and treated early (Healthdirect 2024).
How is Coeliac Disease Treated?
While there is no cure for coeliac disease, symptoms can be managed by consuming a strict gluten-free diet, which will allow the small intestine to heal and stay healthy. This diet must be a lifelong commitment (Healthdirect 2024).
Foods to Avoid

An essential component of maintaining a gluten-free diet is knowing what foods to avoid. Some are obvious, but there are many foods containing gluten that you might not expect.
The following foods contain gluten and should be avoided by people living with coeliac disease (apart from gluten-free alternatives):
- Bread
- Cereal
- Porridge
- Cake
- Biscuits
- Pizza
- Pasta
- Wheaten breadcrumbs or batter
- Pastry
- Wheat-based noodles
- Couscous, semolina and burghul
- Stuffing.
(Better Health Channel 2021)
The following foods may contain gluten, and therefore, people living with coeliac disease should research and read food labels before consuming them:
- Cornflour
- Soy sauce
- Vegemite
- Stock
- Gravy
- Soup
- Malt drinks
- Sauce
- Dressing
- Sausages and hamburgers
- Crumbed and marinated meats
- Smallgoods (e.g. salami)
- Barbequed chicken
- Confectionary
- Ice cream
- Custard powder
- Icing sugar mixture
- Baking powder
- Beer.
(Better Health Channel 2021)
Some medicines may contain gluten. This should be stated on the label (Better Health Channel 2021).
Can Coeliac Disease be Prevented?
There is no way to prevent coeliac disease. The best way to avoid complications is through early diagnosis and strict adherence to a gluten-free diet (Healthdirect 2024).
Test Your Knowledge
Question 1 of 3
How is coeliac disease managed?
Topics
References
- Better Health Channel 2021, Coeliac Disease and Gluten Sensitivity, Victoria State Government, viewed 14 May 2025, https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/ConditionsAndTreatments/coeliac-disease-and-gluten-sensitivity
- Daley, SF & Haseeb, M 2025, ‘Celiac Disease’, StatPearls, viewed 14 May 2025, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441900/
- Healthdirect 2024, Coeliac Disease, Australian Govenment, viewed 14 May 2025, https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/coeliac-disease
- Healthy WA 2018, Coeliac Disease, Western Australia Government, viewed 14 May 2025, https://healthywa.wa.gov.au/Articles/A_E/Coeliac-disease
- Mayo Clinic 2023, Celiac Disease, Mayo Clinic, viewed 14 May 2025, https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/celiac-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20352220
- MedlinePlus 2019, Coeliac Disease, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, viewed 14 May 2025, https://medlineplus.gov/genetics/condition/celiac-disease/
- Pathology Tests Explained 2024, Deamidated Gliadin Antibody (Coeliac Disease Test), Pathology Tests Explained, viewed 14 May 2025, https://pathologytestsexplained.org.au/ptests.php?q=Deamidated+Gliadin+Antibody+%28Coeliac+Disease+Test%29
 New
New 
