360-degree feedback is a comprehensive approach to evaluating employee performance, playing a vital role in learning and development within the healthcare industry. This feedback method involves collecting insights about an employee's performance from a wide range of sources including team members, peers direct reports, and human resources. Its adoption across various sectors, particularly in healthcare, is attributed to its thorough and holistic review mechanism.
What is 360-Degree Feedback?
Also known as multi-rater feedback or 360 review, 360-degree feedback is a development tool utilised in performance management. It uniquely collects feedback from a full circle of reviewers, encompassing a diverse range of perspectives including health professionals. This approach is integral to crafting effective learning and development strategies within organisations, fostering a culture of continuous improvement and self-awareness.
How is 360-Degree Used in Healthcare?
In healthcare, 360-degree feedback is instrumental for care worker training and enhancing the capabilities of support workers. It plays a crucial role in not only enhancing leadership skills but also in improving patient care and service delivery in various settings like primary care, allied health, and other care services.
Examples of 360-Degree Feedback in Healthcare
The implementation of 360-degree feedback in healthcare provides numerous illustrative examples, demonstrating its effectiveness in enhancing both individual and team performance. Here are some expanded examples:
- Nurses' Patient Care: Nurses are often evaluated on their ability to communicate effectively with patients, manage patient care, and work collaboratively with other healthcare professionals. Feedback can be gathered from patients, peers, and supervisors to provide a comprehensive view of their interpersonal skills and clinical competence.
- Doctors' Clinical Skills: For doctors, 360-degree feedback can encompass aspects such as diagnostic accuracy, bedside manner, and collaboration with other medical staff. This feedback, collected from colleagues, nursing staff, and even patients, can provide valuable insights into their professional practice and patient interaction.
- Administrative Staff Efficiency: Administrative personnel in healthcare, responsible for managing patient data and supporting clinical staff, can be assessed on their organisational skills, communication, and ability to handle patient inquiries. Feedback from healthcare professionals they support, as well as from patients, can highlight areas of strength and opportunities for improvement.
- Support Workers' Engagement: For support workers, feedback might focus on their interactions with patients, adherence to care plans, and collaboration with healthcare teams. This feedback can be instrumental in identifying training needs and promoting professional development.
- Leadership in Healthcare Settings: Leaders in healthcare, such as department heads or senior administrators, can be evaluated on their leadership skills, decision-making, and ability to foster a positive work environment. Feedback from direct reports, peers, and superiors can provide a well-rounded perspective on their leadership effectiveness.
Steps to Perform 360-Degree Feedback
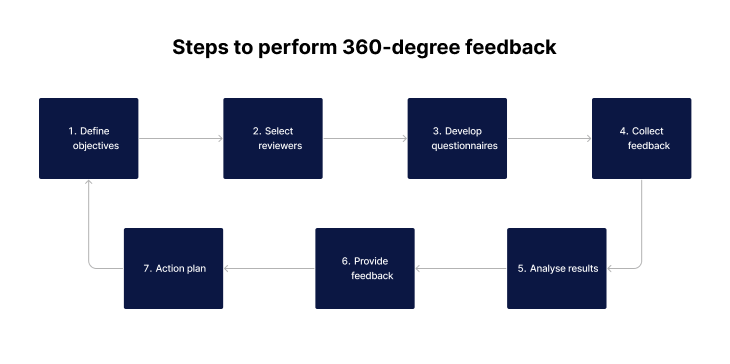
The implementation of a 360-degree feedback process is a strategic approach that involves several key steps. Each step is crucial in ensuring the effectiveness and accuracy of the feedback.
- Define Objectives: The first step involves setting clear, specific goals for the feedback process. This includes identifying the competencies, behaviors, and skills that are most relevant to the healthcare professional's role.
- Select Reviewers: Choosing the right mix of reviewers is critical. This includes peers, direct reports, managers, and sometimes even patients or their families. The diversity of perspectives ensures a well-rounded view of the employee’s performance.
- Develop Questionnaires: Creating well-structured questionnaires with relevant rating scales is essential. These questionnaires should be tailoured to address specific competencies and behaviors relevant to healthcare roles.
- Collect Feedback: Gathering feedback should be done in a way that maintains anonymity and confidentiality, encouraging honest and constructive responses.
- Analyse Results: Analysing the feedback involves looking for trends, strengths, and areas for improvement. This step often requires sophisticated software tools to handle large amounts of data effectively.
- Provide Feedback: Sharing the results with the employee should be done in a constructive manner, focusing on development and growth opportunities rather than criticism.
- Action Plan: Developing an action plan based on the feedback is a crucial follow-up. This plan should include specific steps for the employee to take in order to improve their skills and performance.
Is 360 Degree Feedback Effective?
Benefits and Negatives of Using 360-Degree Feedback
360-degree feedback comes with a range of benefits and potential drawbacks that are important to consider, especially in the sensitive environment of healthcare.
| Benefits | Negatives |
|---|---|
| Provides a comprehensive view of an employee’s performance from multiple perspectives. | Can be time-consuming, requiring careful coordination and follow-up. |
| Enhances self-awareness among healthcare professionals, leading to personal and professional development. | Potential for biased feedback if not properly managed and structured. |
| Encourages a culture of open communication and continuous feedback in healthcare settings. | Risk of negative impact on morale if feedback is not delivered in a constructive manner. |
| Helps identify gaps in skills and training needs, guiding learning and development efforts. | Feedback can be overwhelming if not adequately filtered and focused. |
Tips for Using 360-Degree Feedback Effectively
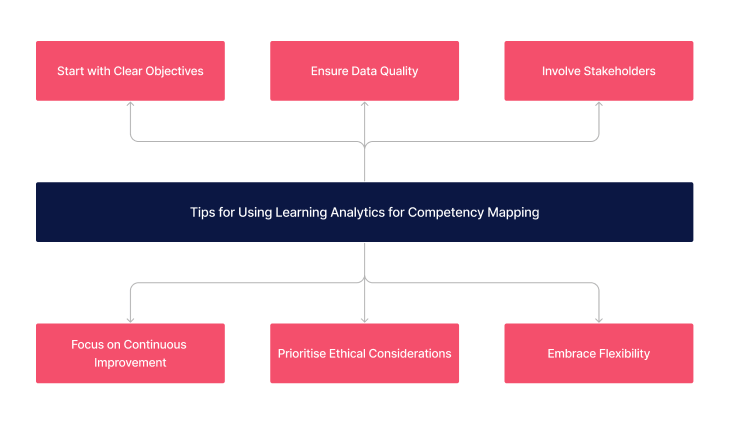
Implementing learning analytics in competency mapping can be complex but rewarding. Here are some tips to make the most of this approach:
- Ensure Anonymity: Maintaining confidentiality is key to obtaining honest and objective feedback.
- Training: Educating staff on how to give and receive feedback constructively is crucial. This involves training on how to interpret feedback, provide constructive criticism, and use feedback for personal development.
- Use as a Development Tool: The primary purpose of 360-degree feedback should be development and growth. It should not be used for punitive measures or as the sole basis for performance evaluations.
- Follow-Up: Implementing a follow-up plan to address the feedback is vital. This includes setting specific goals, providing resources for improvement, and regular check-ins to monitor progress.
- Integration with LMS: Integrating feedback into a learning management system can help track progress over time, align development plans with training programs, and provide a holistic view of a healthcare professional’s growth.
Want a healthcare LMS that aligns 360-degree feedback with L&D?
Contact Ausmed today and see how we can support your organisation!
Tools to Use 360-Degree Feedback
In the realm of healthcare, implementing effective 360-degree feedback necessitates specialised tools designed to facilitate comprehensive and accurate data collection and analysis.
- Advanced HR Software Systems: These offer customised survey functionalities, enabling the collection of feedback from various sources within the healthcare environment.
- Customisable Feedback Forms: tailoured to specific healthcare roles, these forms ensure relevant and focused feedback collection.
- Robust Data Analysis Features: Essential for interpreting the vast amount of data collected, aiding in making informed decisions for employee development.
- Integration with Learning Management Systems (LMS): This feature allows for a streamlined process, aligning feedback with training programs and performance tracking.
- Confidentiality and User-Friendly Interface: Ensuring the privacy of feedback while being accessible to all participants in the feedback process.
Related Resources
- LMS in Healthcare: The Roles, Benefits and Pros and Cons
- What Are Learning Analytics?
- A Step-by-Step Guide to Data Collection for Learning Analytics
- How to Create a Culture of Continuous Learning
- Guide to Building a Competency Framework for Skill Development
- How to Manage an Effective Staff Training Program
- Identifying Skills Gaps with Learning Analytics
- Conducting "Pre-Training Interviews" Before Education
Conclusion
Using learning analytics in competency mapping presents a significant opportunity for educational institutions and healthcare organisations to enhance their workforce's skills and performance. By adopting a data-driven approach, they can ensure their training programs align with the demands of quality healthcare provision. This innovative approach promises to create a more competent, skilled, and responsive healthcare workforce.
References
- Carney, P. A., Sebok-Syer, S. S., Pusic, M. V., Gillespie, C. C., Westervelt, M., & Goldhamer, M. E. J. (2023). Using learning analytics in clinical competency committees: Increasing the impact of competency-based medical education. Med Educ Online, 28(1), 2178913. https://doi.org/10.1080/10872981.2023.2178913.
- Thoma, B., Ellaway, R. H., & Chan, T. M. (2021). From Utopia Through Dystopia: Charting a Course for Learning Analytics in Competency-Based Medical Education. Academic Medicine, 96(7S), S89-S95. https://doi.org/10.1097/ACM.0000000000004092.
- Bojic, I., Mammadova, M., Ang, C. S., Teo, W. L., Diordieva, C., Pienkowska, A., Gašević, D., & Car, J. (2023). Empowering Health Care Education Through Learning Analytics: In-depth Scoping Review. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 25, e41671. https://doi.org/10.2196/41671.



