A Foundation for Clinical Governance and Consumer Safety
Risk management systems are fundamental to providing safe, effective, high-quality care across aged care and healthcare organisations. They are regulatory requirements and core components of good governance, consumer protection, and continuous improvement.
This Training Requirement outlines the regulatory expectations related to risk management and helps organisations translate these expectations into actionable system and workforce initiatives.
Read our article: Action 2.9.5 – What is an Effective Training System? for guidance on building and reviewing effective training systems to support implementing standards like this one.
Using this Training Requirement
This resource guides understanding and operationalising the specific actions related to risk management systems within the:
- National Safety and Quality Health Service (NSQHS) Standards
- Strengthened Aged Care Quality Standards (2025)
It outlines:
- Key regulatory requirements
- System and workforce responsibilities
- When training or education is appropriate
- What evidence may be requested in an audit
While education is one enabler of compliance, it is not sufficient alone. Organisations must also maintain clear policies, robust procedures, and transparent records that support consistent, effective, and organisation-wide risk management.
Understanding the Relevant Actions in the Standards
NSQHS Standards
Action 1.10 – Risk Management System
The health service organisation must:
- Identify, assess and document risks
- Use data and reporting to support risk reviews
- Implement actions to reduce risk
- Plan for and respond to internal/external emergencies
- Review the risk system’s effectiveness
- Communicate risk to the workforce and consumers
Strengthened Aged Care Quality Standards
Outcome 2.4 – Risk Management System
The provider is required to establish and maintain a risk management system that:
| Action | Focus |
|---|---|
| 2.4.1 | A documented risk management system is in place covering risks to consumers, staff, operations and systems |
| 2.4.2 | Strategies are in place to prevent, control, minimise or eliminate risks |
| 2.4.3 | Risks are communicated to older people using appropriate, accessible methods |
| 2.4.4 | The system is regularly reviewed and improved, with changes documented and implemented. |
Accountability for Risk Management
Governing Body Accountability
The Board or governing body is accountable for the organisation’s risk management framework. They must ensure appropriate systems are in place and regularly reviewed to maintain oversight of risks to people, operations, and the environment.
Operational Accountability
Implementation sits with key functional leads—often the Quality, Clinical Governance, and People & Culture teams—who:
- Document and monitor organisational risk
- Lead risk assessments and quality improvement activities
- Report to governance bodies
- Support staff to understand their role in risk mitigation
Workforce Roles and Responsibilities
All staff have a duty to:
- Escalate and document risks
- Follow organisational protocols
- Contribute to system improvements through feedback and incident reporting
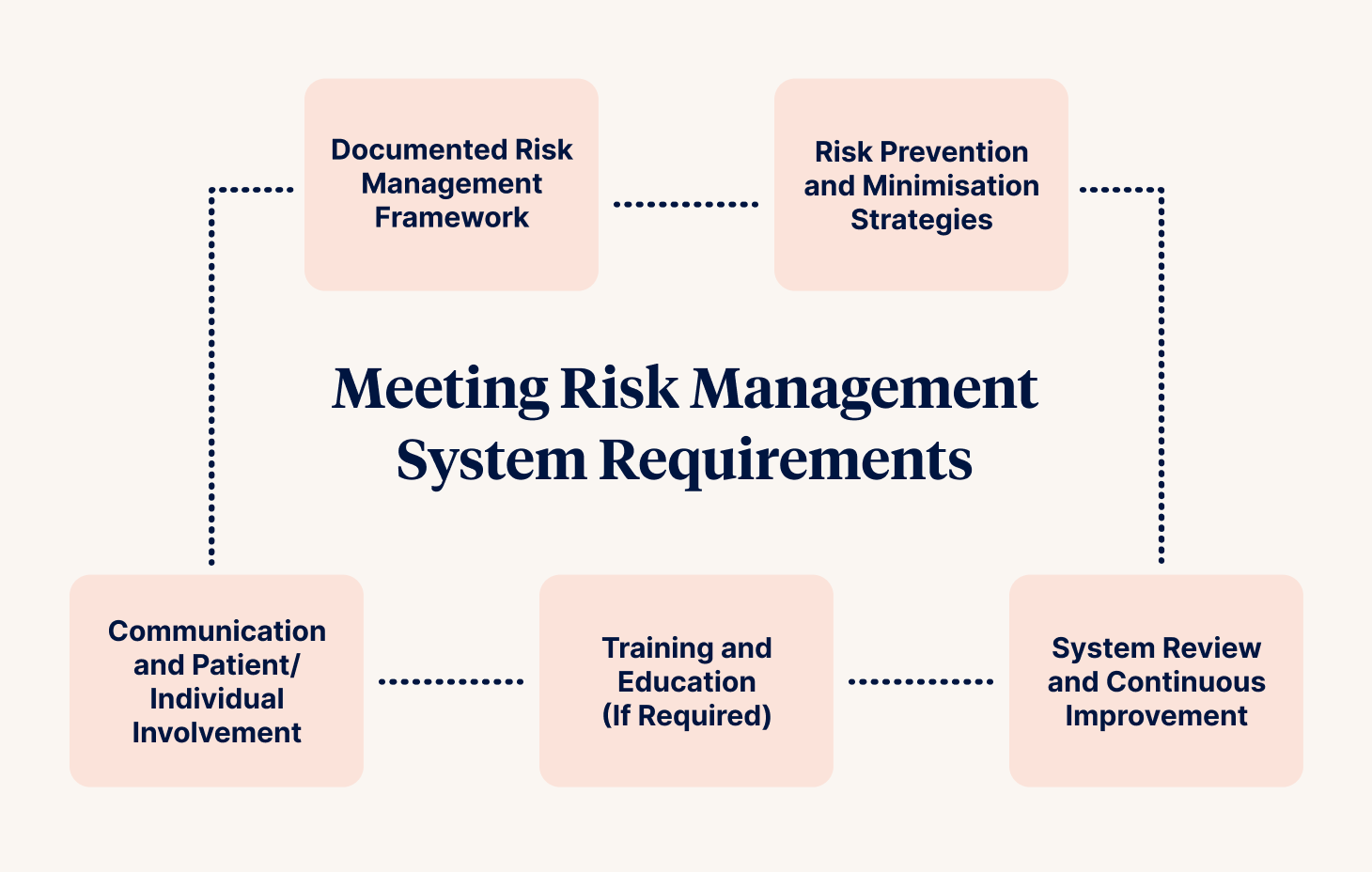
Meeting Risk Management System Requirements
To meet the standards, organisations should maintain a robust and transparent risk management system with the following components:
1. Documented Risk Management Framework
- A clearly defined, organisation-wide risk management policy
- Defined responsibilities for identifying, escalating and mitigating risk
- A current and regularly reviewed risk register
- Processes covering business continuity, clinical risks, worker safety and system security
2. Risk Prevention and Minimisation Strategies
- Preventive measures built into care processes, workforce systems and physical environments
- Clear procedures for controlling and minimising risk (e.g., PPE protocols, safe work practices)
- Workforce awareness of risk prevention procedures, especially in high-risk roles
3. Communication and Patient/Individual Involvement
- Consumers are informed of relevant risks and supported to participate in risk planning (e.g., dignity of risk discussions)
- Documentation of how communication is tailored to meet cultural, cognitive or linguistic needs
4. System Review and Continuous Improvement
- Scheduled reviews of the risk management system
- Use of risk, incident, and feedback data to drive improvements
- Documented governance oversight and changes made
5. Training and Education (If Required)
Training may be appropriate when:
- Staff are expected to use or lead elements of the risk management system
- New policies or procedures are introduced
- Staff are in roles responsible for high-risk areas (e.g., infection control, emergency planning)
Training may include:
- How to conduct a risk assessment
- How to report and escalate risks
- Role-specific training on implementing control measures
- Onboarding for Board and governance members on risk responsibilities
Evidence of Compliance
Organisations can demonstrate a robust and effective approach to policy and procedure management by referring to detailed lists of evidence that may be audited:
- Strengthened Aged Care Quality Standards Evidence Mapping Framework (the auditor's tool)
- NSQHS Standards Action 1.07 Strategies for improvement
The following items are identified as items auditors may request to assess the effectiveness of your policy and procedure system:
| Requirement | Evidence Examples |
|---|---|
| Risk System Design | Risk management policy and procedures; clearly defined roles and responsibilities |
| Risk Identification | Risk register, incident logs, and documentation of emerging risks |
| Control Measures | Updated procedures or protocols following risk assessments |
| Communication to Clients | Consumer communication plans, examples of tailored communication, and participation in risk planning |
| System Review | Meeting minutes showing risk system review, action plans, or evidence of system improvements |
| Training Records | Evidence of staff or board training in risk identification, assessment or mitigation |

Ensure your organisation is prepared for your first audit under the strengthened Standards.
Embedding Risk Management
Risk management is central to the governance and quality frameworks in the Strengthened Aged Care Quality Standards and the NSQHS Standards. These systems protect the rights, safety, and well-being of older people and help organisations prevent harm, respond to emerging challenges, and continuously improve.
Meeting the risk management training requirement means more than delivering one-off training. It requires embedding risk awareness into your systems, building staff capability, and maintaining visible governance oversight.
When done well, risk management becomes a lever for improving care, not just avoiding it from going wrong.
Relevant Resources
Explore our Guide to Ausmed’s Audit Readiness Tool for a structured approach to meeting evidence requirements.
Watch our webinar, Getting Your Training System Ready for an Audit, for a detailed look at how training, learning, and development requirements align with audit expectations.
- Strengthened Aged Care Quality Standards - Aged Care Quality and Safety Commission
- Strengthened Quality Standards Provider Guidance - Aged Care Quality and Safety Commission
- Evidence Mapping Framework - Aged Care Quality and Safety Commission



