What is Blended Learning?
Blended learning is a dynamic educational strategy that combines online digital media with traditional classroom methods. It requires the physical presence of both teacher and student, while offering flexibility in terms of time, place, path, or pace of learning. This approach optimises the learning process by combining the immediacy and interactivity of classroom learning with the resource-rich, self-paced nature of online learning. It adapts to different learning styles, making the educational experience more personalised and engaging. This method is particularly effective in catering to adult learners, like healthcare professionals, who benefit from the autonomy and convenience of online resources alongside the structured support of face-to-face instruction.
Blended Learning in Healthcare
In the fast-evolving healthcare sector, blended learning addresses the need for ongoing professional development and adaptable training methods. It integrates face-to-face instruction with digital technologies, such as online courses, interactive simulations, and virtual reality experiences, to provide a comprehensive learning experience. This blending is invaluable in complex fields like healthcare, where theoretical knowledge and practical skills are equally important. For instance, a nurse in aged care might use online modules to study the latest care techniques and participate in in-person workshops to practice these skills, thereby gaining a holistic understanding of patient care.
Positives and Negatives of Self-Directed Learning Strategies
Self-directed learning empowers healthcare professionals to take control of their educational journey, fostering a sense of ownership and motivation. This autonomy is crucial for lifelong learning and adapting to the ever-changing healthcare landscape. However, self-directed learning can also pose challenges, such as the risk of learners feeling isolated or overwhelmed without adequate support. To mitigate these challenges, it is essential to provide access to resources, mentorship, and a supportive learning community. This support helps maintain motivation and ensures that learners can effectively navigate and benefit from the flexibility offered by self-directed learning.
| Positives | Negatives |
|---|---|
| Enhances learner autonomy and motivation | Potential for feelings of isolation |
| Facilitates lifelong learning and adaptability | Risk of becoming overwhelmed without structured guidance |
| Allows for personalised learning pace and style | Requires high levels of self-discipline and time management |
Importance of Blended Learning in Healthcare
Blended learning is vital in healthcare for several reasons. Firstly, it provides flexible training options that can be tailored to individual schedules, crucial for busy healthcare professionals. Secondly, it accommodates various learning preferences, from visual and auditory to kinesthetic, enhancing the overall effectiveness of training. Thirdly, it allows for the immediate application of learned skills in a clinical setting, bridging the gap between theory and practice. This approach is essential in maintaining high standards of patient care and keeping up with advancements in medical knowledge and technology. Blended learning also plays a pivotal role in promoting teamwork and collaborative skills among healthcare workers, as it often involves group work and peer-to-peer learning activities.
Examples of Blended Learning
Examples of blended learning in healthcare are diverse. For instance, online modules may cover the theoretical aspects of patient care, while face-to-face sessions focus on practical skills like CPR or wound care. Another example is the use of virtual simulations for surgical training, combined with real-life surgical observations or practice. These methods ensure a comprehensive understanding of both the knowledge and skills required in healthcare.
| Blended Learning Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Theoretical Online Modules | Covering aspects of patient care, medical procedures, and healthcare policies. |
| Practical Hands-On Workshops | Focus on skills like CPR, wound care, and patient handling. |
| Virtual Simulations | For surgical training, diagnostics, and emergency response scenarios. |
| Interactive Case Studies | Online case studies followed by group discussions and practical sessions. |
How to Apply Blended Learning (Steps)
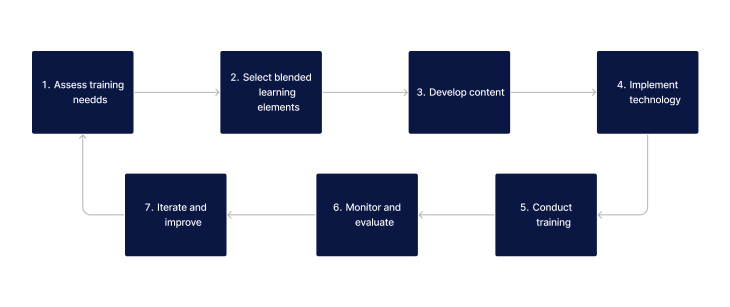
Applying blended learning effectively in the healthcare sector involves a series of steps to ensure a balanced and comprehensive approach. This methodical process helps in creating a learning environment that is both effective and engaging.
- Assess Training Needs: Identify the specific learning needs and goals of the healthcare program. This could involve understanding the skill gaps, learning preferences, and logistical considerations of the learners.
- Select Blended Learning Elements: Choose the appropriate mix of online and traditional teaching methods. This might include online lectures, interactive e-learning modules, hands-on practical sessions, and peer collaboration activities.
- Develop Content: Create or curate content for both online and face-to-face components. Ensure that the content is relevant, engaging, and aligned with the learning objectives.
- Implement Technology: Utilise a robust learning management system (LMS) to facilitate online aspects of the training, including content delivery, communication, and progress tracking.
- Conduct Training: Execute the blended learning program, ensuring a seamless integration of online and traditional elements. Provide ongoing support to learners throughout the training period.
- Monitor and Evaluate: Continuously assess the effectiveness of the blended learning program. Gather feedback from learners and educators, and make adjustments as necessary to improve the learning experience.
- Iterate and Improve: Regularly update and refine the blended learning approach based on feedback, technological advancements, and changes in the healthcare field.
Want a healthcare LMS that can support blended learning strategies?
Contact Ausmed today and see how we can support your organisation!
Tips for Implementing Blended Learning
- Define clear learning outcomes and align content accordingly.
- Choose a mix of online and face-to-face elements that complement each other.
- Invest in a robust learning management system for efficient content delivery and progress tracking.
- Regularly update content to reflect the latest healthcare practices and research.
- Provide continuous support and feedback to learners.
- Encourage collaboration and interaction among learners to build a community of practice.
- Integrate real-world case studies and scenarios to enhance practical understanding.
- Ensure accessibility and ease of use for all technology and materials used.
Related Resources
- LMS in Healthcare: The Roles, Benefits and Pros and Cons
- A Guide to Self-Directed Learning
- How to Create a Culture of Continuous Learning
- How to Manage an Effective Staff Training Program
- Identifying Skills Gaps with Learning Analytics
- A Guide to Personalised Learning in Healthcare
Conclusion
Blended learning represents a significant advancement in healthcare education, offering a flexible, efficient, and effective approach to professional development. By combining the best of both online and traditional methods, it prepares healthcare professionals for the multifaceted challenges of modern healthcare delivery. Embracing this approach is key to fostering a skilled, adaptable, and resilient healthcare workforce, capable of delivering high-quality care in an ever-evolving landscape. Ultimately, blended learning is not just about imparting knowledge; it's about creating an environment where healthcare professionals can continuously grow, adapt, and excel in their roles.
References
- Garrison, D. R., & Kanuka, H. (2004). Blended learning: Uncovering its transformative potential in higher education. The Internet and Higher Education, 7(2), 95-105.
- Means, B., Toyama, Y., Murphy, R., Bakia, M., & Jones, K. (2010). Evaluation of Evidence-Based Practices in Online Learning: A Meta-Analysis and Review of Online Learning Studies. U.S. Department of Education.
- Porter, W. W., Graham, C. R., Spring, K. A., & Welch, K. R. (2014). Blended learning in higher education: Institutional adoption and implementation. Computers & Education, 75, 185-195.
- Edwards, R., & Usher, R. (2008). Globalisation and Pedagogy: Space, Place and Identity. Routledge.



