What is Face-to-Face Training?
Face-to-face training in healthcare involves direct interaction between educators and learners, enabling real-time feedback, clarification of health information, and fostering personal connections. This traditional method emphasises the importance of body language and personal engagement in learning. At its core, face-to-face training encompasses a variety of interactive methodologies, including live demonstrations, hands-on practice, role-playing scenarios, and group discussions.
How Does Face-to-Face Training Occur in Healthcare?
In healthcare, face-to-face training is delivered through structured training sessions, workshops, and seminars. These sessions are designed for health professionals including allied health, primary care providers, and health services staff, focusing on practical skills, patient interaction, and immediate feedback.
Examples of Face-to-Face Training in Healthcare:
- Clinical skills workshops for healthcare professionals: Led by experienced practitioners, these sessions not only focus on the practical skills but also on understanding the underlying principles and protocols, ensuring patient safety, and improving outcomes
- Emergency response drills for hospital staff: These drills simulate real-life scenarios, requiring participants to apply their knowledge and skills in high-pressure situations.
- Simulations for all healthcare workers: These simulations use mannequins, actors, or virtual reality to replicate clinical situations, allowing individuals to practice assessment, treatment planning, and intervention strategies.
How an LMS Can Enhance Face-to-Face Training in Healthcare Education
A Learning Management System (LMS) can complement face-to-face training by providing online resources, enabling blended learning, and facilitating the tracking of progress and certification. LMS platforms support the Australian health education ecosystem by offering access to a wide range of online learning materials and health information.
Steps to Implement Face-to-Face Training
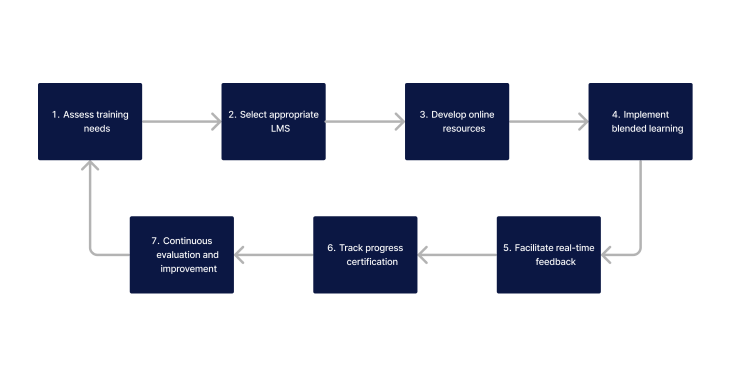
Integrating a Learning Management System (LMS) into face-to-face training programs can significantly elevate the quality and efficiency of healthcare education. Here are key ways in which an LMS achieves this enhancement:
- Assess Training Needs: Identify the specific training needs of healthcare professionals, including areas where online resources can complement face-to-face learning.
- Select an Appropriate LMS: Choose an LMS that fits the requirements of the healthcare education landscape, with robust support for online materials and health information.
- Develop Online Resources: Create or curate online learning materials that align with the objectives of face-to-face training sessions, ensuring they are relevant and up-to-date.
- Implement Blended Learning: Integrate online resources with traditional training methods, using the LMS to facilitate a seamless blend of digital and in-person education.
- Facilitate Real-Time Feedback: Utilise the LMS to provide real-time feedback on online assessments, enhancing the learning experience and allowing for immediate clarification and improvement.
- Track Progress and Certification: Employ the LMS's tracking capabilities to monitor learner progress, manage assessments, and issue certifications upon successful completion of training modules.
- Continuous Evaluation and Improvement: Regularly review and update the online and face-to-face components of the training program, based on feedback and the evolving needs of the healthcare sector.
Tips for Implementing a Learning Management System that enhances face-to-face training
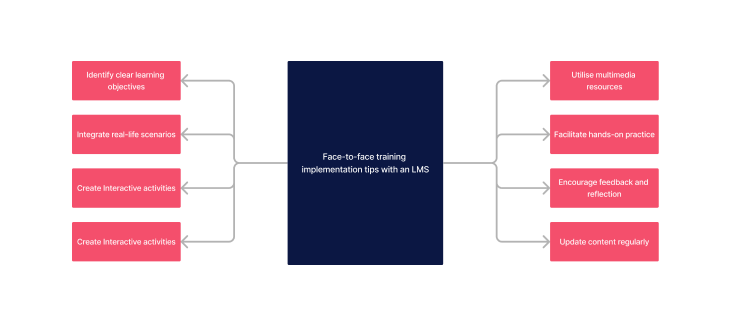
Implementing an LMS in healthcare education comes with its unique set of challenges and opportunities. Here are some tips to ensure a smooth and effective implementation process, drawing from best practices and common pitfalls to avoid.
- Identify clear learning objectives: Define specific, measurable outcomes you expect learners to achieve. This clarity helps in structuring the entire session around achieving these goals, ensuring that all activities and materials are purposefully directed towards these ends.
- Integrate real-life scenarios: Incorporating case studies or scenarios that reflect actual situations faced in healthcare settings makes the learning experience more relatable and valuable. It helps learners envision how to apply theoretical knowledge in real-world contexts, enhancing their problem-solving and decision-making skills.
- Create interactive activities: Activities requiring active engagement, such as role-plays, simulations, and discussions, foster a deeper understanding of the subject matter. These interactive elements encourage participation, critical thinking, and the practical application of concepts learned.
- Incorporate current health system guidelines: Aligning training content with the most recent healthcare guidelines ensures that learners are up-to-date with best practices and regulatory standards. This relevance is crucial for maintaining the quality and safety of patient care.
- Utilise multimedia resources: Different learners have different learning styles. Incorporating a variety of multimedia resources, such as videos, images, and digital content, can cater to these diverse preferences, making learning more accessible and engaging for everyone.
- Facilitate hands-on practice: Practical exercises allow learners to apply what they've learned in a tangible way. By practicing skills in a controlled setting, learners gain confidence and competence that will be invaluable in their professional roles.
- Encourage feedback and reflection: Creating opportunities for feedback allows learners to understand their progress and areas for improvement. Reflection on the learning process and outcomes fosters a mindset of continuous professional development and growth.
- Update content regularly: Healthcare is a rapidly evolving field. Regularly reviewing and updating training materials ensures that the content remains relevant, accurate, and reflective of the latest advancements and research findings in the healthcare sector.
Need a new healthcare LMS that can enhance the face-to-face training in healthcare education?
Contact Ausmed today and see how we can support your organisation!
Advantages and Disadvantages of healthcare LMS that can enhance the face-to-face training in healthcare education
This table outlines the key advantages and disadvantages of face-to-face training in healthcare. It highlights the benefits of direct interaction and challenges related to scale and logistics, providing a balanced view of this training approach.
| Benefits | Negatives |
|---|---|
| An LMS allows learners to access educational content anytime, anywhere, making it easier to fit learning into busy schedules | Reliance on an LMS means that technical issues can hinder access to learning materials and disrupt the educational process. |
| LMS platforms can host a wide array of multimedia resources, including videos, interactive simulations, and digital libraries, enriching the learning experience. | Implementing an LMS can be expensive, requiring significant upfront investment in software, hardware, and training. |
| educators can tailor the learning experience to meet individual learner needs, accommodating different learning styles and paces. | Both educators and learners may face challenges in adapting to the LMS, necessitating additional time and resources for training. |
| LMS platforms offer tools for tracking progress and assessing performance, providing valuable data for both learners and educators to improve learning outcomes | Overreliance on an LMS for content delivery can reduce opportunities for personal interaction, which is crucial for developing communication skills and professional relationships. |
Related Resources
- Mandatory Training: How an LMS can help you meet requirements
- LMS in Healthcare: The Roles, Benefits and Pros and Cons
- LMS in Disability Care: The Roles, Benefits and Pros and Cons
- What Is the Role of an LMS in Aged Care?
- What Are Learning Analytics?
- How to Create a Culture of Continuous Learning
- Guide to Compliance Training (for Healthcare Managers)
- Guide to Building a Competency Framework for Skill Development
- How to Manage an Effective Staff Training Program
- Identifying Skills Gaps with Learning Analytics
- How Do I Use Learning Analytics for Competency Mapping?
- A Guide to Personalised Learning in Healthcare
Conclusion
Integrating a Learning Management System (LMS) with traditional face-to-face training methods can significantly enhance healthcare education. This blended approach ensures that health professionals receive comprehensive, engaging, and effective training that aligns with the evolving needs of the Australian healthcare system.
References
- Janes, G, Ekpenyong, MS, Mbeah-Bankas, H. and Serrant, L, 2023. An international exploration o
- Keis, O, Grab, C, Schneider, A, and Öchsner, W, 2017, Online or face-to-face instruction? A qualitative study on the electrocardiogram course at the University of Ulm to examine why students choose a particular format, BMC medical education, vol.17, no.194, pp.1-8.
- Singh, J, Steele, K, and Singh, L, 2021, Combining the best of online and face-to-face learning: Hybrid and blended learning approach for COVID-19, post vaccine, & post-pandemic world, Journal of Educational Technology Systems, vol.50, no.2, pp.140-171, https://doi.org/10.1177/00472395211047865



